This study sets out to provide a comparison on some aspects of the role of training to trainers and teachers between two groups. The comparison is conducted by using a questionnaire that has been used as a tool to collect related data and to fill in a clear information gap about how it is developing and people’s opinions, to provide some understanding of the current state and some of future directions of the related aspects.
Table of Contents
With the rapidly increasing popularity of the Internet in recent years, there is an increasing demand for methodologies and technologies, especially for e-learning. E-learning is interactive learning in which the learning content is available on-line and provides automatic feedback to the student’s learning activities. Therefore, there is an increasing demand for methodologies and technologies, especially for e-learning. e-learning is defined as interactive learning in which the learning content is available on-line and provides automatic feedback to the student’s learning activities.
Study on the Role of Training to Trainers and Teacher
While recognizing that the world at large will continue to use terminology in different and often ambiguous ways, the term of e-learning is used here to refer to on-line interactions of various kinds including on-line that takes place between learners and instructors. E-learning is learning supported by Information and Communication Technologies (ICT). It is not limited to digital literacy. It may include multiple formats and hybrid methodologies such as the use of software, Internet, online learning or any other electronic or interactive media.
Although it is the potential this has for improving both the quantity and quality of learning. Improving both the quantity and quality of interaction among teachers and students and between students and accelerating the adoption of new and more information and programs.
For instead the motivation to start learning is as important with e-learning as with other media. The proper will compare different features of e-learning in the Eastern side and make recommendations for the introduction of e-learning in the Eastern side.
In order to compare between the and the Eastern side on several directions in the field of e-learning, a questionnaire was developed based on indicators found in Cede fop online surveys and work done in cooperation with (Lahwal ., et.al 2009, 2016, 2021).The indicators (questionnaire items) were modified to directly tap into each of the sides of the learning field that takes place between learners and instructors.
E-learning is learning supported by Information and Communication Technologies (ICT). It is not limited to digital literacy. It may include multiple formats and hybrid methodologies such as the use of software, Internet, CD-ROM, online learning or any other electronic or interactive media. Although it is the potential this has for improving both the quantity and quality of learning. Improving both the quantity and quality of interaction among teacher and student and between students, and accelerating the adoption of new and more information and programs.
2. Literature Review
This study provides a review from the papers that concern the e-learning technologies in the information and communication technology environment to be used for comparison between western and Arabic countries.
This review only focuses on the more recently published papers. This is to get the newest knowledge on how the engineering or information and communication technology applied the e-learning technology into their environment and tries to find out the advantages that they obtained from the comparison of this technology.
Lewis and Whitlock believe that e-learning is no longer new. It fills a growing role in most education and organizations. It makes the lives of individuals easier, helping people learn whilst at work or in the home, flexibly and at times that suit them. It also meets corporate objectives for cost effective training and for introducing new procedures quickly. As technology and software improve, e-learning is becoming faster, more reliable, more portable and easier to use.
E-learning in higher education is a developing area for study in modern institutions. For the purposes of the research, Massy defines e-learning as ‘learning supported by information and communication technologies (ICT)’. It is not limited to digital literacy. and may encompass multiple formats and hybrid methodologies such as the use of software, online learning or any other electronic or interactive media.
Joachim, Werner and Dirk explain that traditional means of education are no longer enough to meet the needs of lifelong learning. Even where available, the quality of education does not meet the high standards of international business and also point to many countries’ public and private funding for educational services are declining while costs rise faster than income levels.
Therefore, electronic education became a major source for ongoing education in the international knowledge-based economy. It changed public opinion about how much education is necessary, and when and where learning and training can take place.
For instance, once education is a purely local affair, due to not enough enrolment highly specialized courses are not viable sometimes. There are also many people who would like to take courses but who do not have the time or cannot commit to attending a regular class. So, e-learning aims to encourage collaboration between education and training institutions. Motivation to start learning, and to continue it, is as important with e-learning as with other media.
The project will compare different directions of e-learning in the Western and the Arabic side and make recommendations for the introduction of e-Learning in Libya. In order to compare between the UK and the Arab side in several directions in the field of e-learning, a questionnaire was developed based on indicators found in Cedefop online surveys and work done in cooperation with Massy (2002).
3. The Role of Training to Trainers and Teachers
This comparison aims to choose suitable principles of trainer’s skills of e-learning for consideration in this study. The comparison focuses on two kinds of principles.
The first is the level of e-learning skills, technical specification, pedagogical specification, working in a cooperative virtual environment, and how important do trainers rate each of these skills.
The second is acquisition of these skills, including Formal education and training programmes, learned through participation in e-learning activities with others who have formal training in e-learning, learned through trial and error without formal expertise being, or have not acquired any of these skills to date.
Nevertheless, Clarke suggests that e-learning will become central to the knowledge economy with the development of e-learning products and services. However, he points it is necessary to remove fears, two connected believe imagination that are both misleading and causing harm such as:
- The imagination that e-learning represents a more cost effective mode of training and education, and also he points out that e-learning involves at least as much, if not more financial investment, than traditional modes of education and training.
- The imagination that e-learning involves the obsolescence of universities and training colleges.
He also points out that e-learning does not represent a cheap alternative, which makes traditional education and training investment redundant.
Clarke believes that, to providing the most fulfilling forms of educational and training experience, the existence of universities and colleges will remain necessary, but also for developing the technology and content of the e-learning industry (Clarke 2001).
On the other studies, Alexander and McKenzie, for instance, have reported that e-learning would fail for the following reasons (Alexander at el1998): overly achievement in terms of wonted outcomes for the budget and time available; and failed to obtain copyright clearance. The usefulness of particular information technologies for their own sake, without sufficient regard for appropriate learning design.
No change in the assessment of learning to suit the changed learning outcomes; commenced software development without adequate planning. Failed to prepare students for participation in learning experiences such as working in groups. The new emergence of widespread application of computer-based education and training, as well as distance education in many parts of the world is an indication that academia and industry have welcomed technology as a method of making education and training more effective, flexible, efficient and immediate.
The demand for flexible access to learning and the need to overcome skills gaps with development technologies and processes has stimulated the increasing application of computer and communications systems to the delivery of education and training. In the meantime a technology called streaming is alleviating the problem for transmitting video, audio and animation sequences, where an application or file is broken down into small pieces and delivers the of the application while at the same time sending the other compressed pieces.
Hall and Steed believe that security is an important aspect of e-learning technology, and a major area of worry for scents. If company training involves sensitive company information, or if payment is necessary over the Internet, then a greater amount of security should be used. Solutions to this are being improved by the telecommunications industries.
4. Methodology
The methodology applied in this research work is survey-based. A questionnaire was used as the main instrument to collect data. The questionnaire was designed to collect information on the role of training to trainers and teachers in both groups.
The research population consisted of trainers and teachers from the two groups. The sample was selected randomly, ensuring representation of both groups. Data was collected using both online and paper-based questionnaires.
The questionnaire items were divided into several sections that covered various aspects such as the level of e-learning skills, technical specification, pedagogical specification, cooperative virtual environment, skill acquisition and importance rating.
The responses were analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistical techniques to compare the two groups.
5. Comparative Study
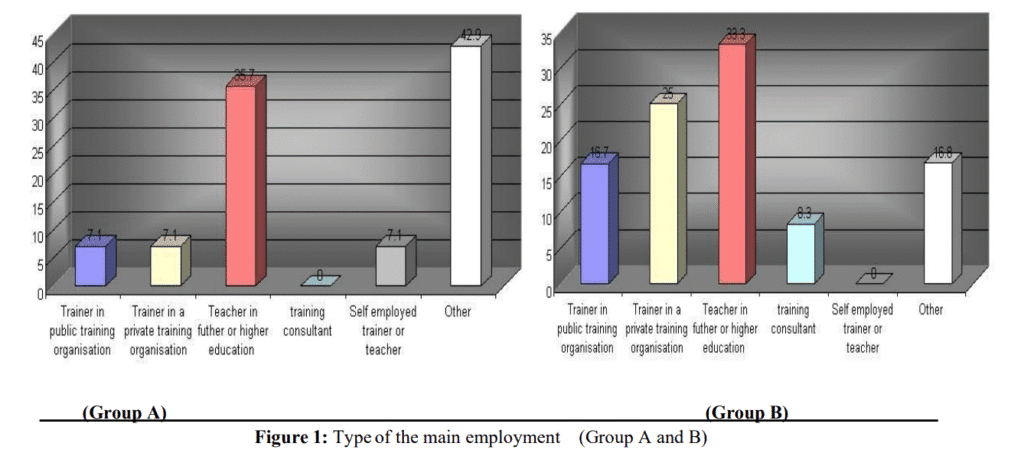
Both groups showed awareness of e-learning technologies. However, the Western group demonstrated higher proficiency in technical specifications and pedagogical approaches. The Eastern group, on the other hand, exhibited stronger motivation toward adopting cooperative virtual environments but lacked structured training mechanisms.
The Western trainers were found to have better access to formal training programs, workshops, and online certifications that enhanced their e-learning skills. In contrast, the Eastern trainers relied more on informal methods such as trial and error and peer learning.
When asked about how they acquired e-learning skills, the Western group indicated that most of their learning came from formal education and institutional training. Meanwhile, the Eastern group relied largely on experiential learning and self-study without formal guidance.
Motivation levels were high in both groups, but for different reasons. The Western group viewed e-learning as a tool for efficiency and flexibility in teaching, whereas the Eastern group saw it as a modern necessity to bridge the digital divide.
The analysis revealed that both groups faced several barriers in implementing e-learning effectively, including lack of technical infrastructure, limited access to high-speed Internet, resistance to change among senior trainers, insufficient time for developing e-learning materials, and lack of security and copyright concerns.
6. Discussion
The study found that training plays a vital role in equipping trainers and teachers with necessary e-learning skills. The Western trainers benefited from structured programs, institutional policies, and advanced technology adoption.
In contrast, the Eastern trainers demonstrated enthusiasm but lacked the same level of institutional and technical support. Institutions in the Western side have long established frameworks that support continuous professional development.
Technical barriers such as poor Internet connectivity and lack of multimedia tools continue to hinder progress in many Eastern educational institutions. Cultural attitudes toward technology and teaching methods also influence adoption.
7. Conclusion and Future Work
The study concludes that training is a crucial factor in the successful implementation of e-learning. The comparative analysis between the two groups revealed that while both share similar goals, their methods, resources, and outcomes differ significantly.
The Western side has achieved maturity in adopting e-learning technologies through structured training and institutional support. The Eastern side shows potential but requires targeted interventions to overcome barriers.
Future work should focus on developing customized training modules, establishing collaborative networks, and promoting exchange programs between the two groups. Additionally, further studies can investigate the long-term impact of e-learning training on teaching effectiveness and student performance.
More Post
- Strengthening Inclusive Teacher Education: From RPD Act 2016 to Practice
- Challenges and Ethical Decision-Making in Management
- Data Privacy in EdTech: A 2025 Policy Playbook for Schools and Districts
Hi, I’m Anshul Patel, author and co-founder of TigerJek.com. I am a long-time Roblox and mobile gaming enthusiast with 6+ years of gameplay experience. I test every method, build, and strategy personally before writing guides for TigerJek. My goal is to simplify complex games and help players progress faster.




